Notes: Quoted from the web site of Japan Financial Services Association as of Oct. 2023.
History of money lending industry in Japan
More than 30 years
ago, there was the times when there were nearly 29 times as many money lenders
nationwide as there are now, and it was even said that there were as many soba (noodle)
shops as there were. There are some money lenders that were lack of awareness of legal
compliance, and the troubles they caused had been highlighted, and the image of the
industry as a whole had been tarnished. The impression of the industry from that time
remains deep-rooted in everyone's minds.
However, those impressions are a thing
of the past.
In fact, the environment of the moneylending industry has changed
completely due to the revision of the Moneylending Business Act in June 2010.
The
revision to the Money Lending Business Act have made it impossible for unqualified
people to enter the money lending industry, and systems have been put in place to
prevent consumers from borrowing too much.
Moreover, Japan Financial Services
Association, a self-regulatory body for the industry, was newly established to set its
own rules and instruct its member money lenders to comply with laws and voluntary rules
through audits and other means.
Now that laws and regulations are in place and money
lenders are becoming more aware of legal compliance, the money lending industry no
longer has the image it used to have.
Background of revision of Money Lending Business Act
The Money Lending Business Act was revised and promulgated in December
2006 to deal with the increasingly serious problem of multiple debts.
The multiple
debts problem was caused by high interest rates, excessive lending, ease of borrowing,
repayment schedule with no interest burden, and lack of financial knowledge and planning
on borrowers. The law was revised to take drastic and comprehensive measures to address
the problem of multiple debts.
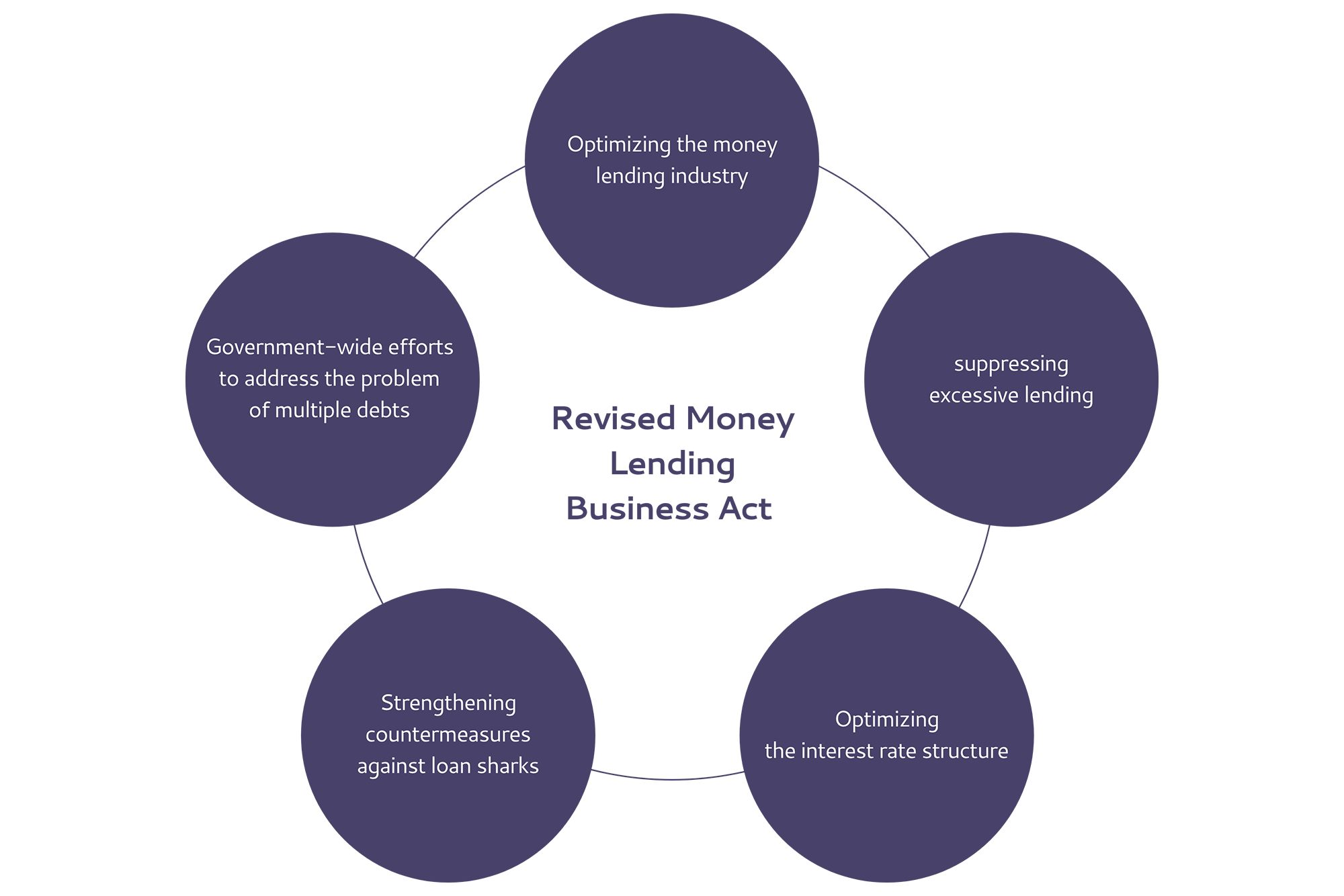
The contents of the revision are divided into
optimizing the money lending industry, suppressing excessive lending, optimizing the
interest rate structure, strengthening countermeasures against loan sharks, and
government-wide efforts to address the problem of multiple debts, to prevent a sudden
impact on borrowers. The law was implemented in four stages over a period of about three
and a half years after its promulgation, as it required time for lenders to prepare
their systems.
In addition to eliminating unqualified lenders, the revision placed
emphasis on improving and streamlining the operations of money lenders, and positioned
money lenders as important players in the financial market.
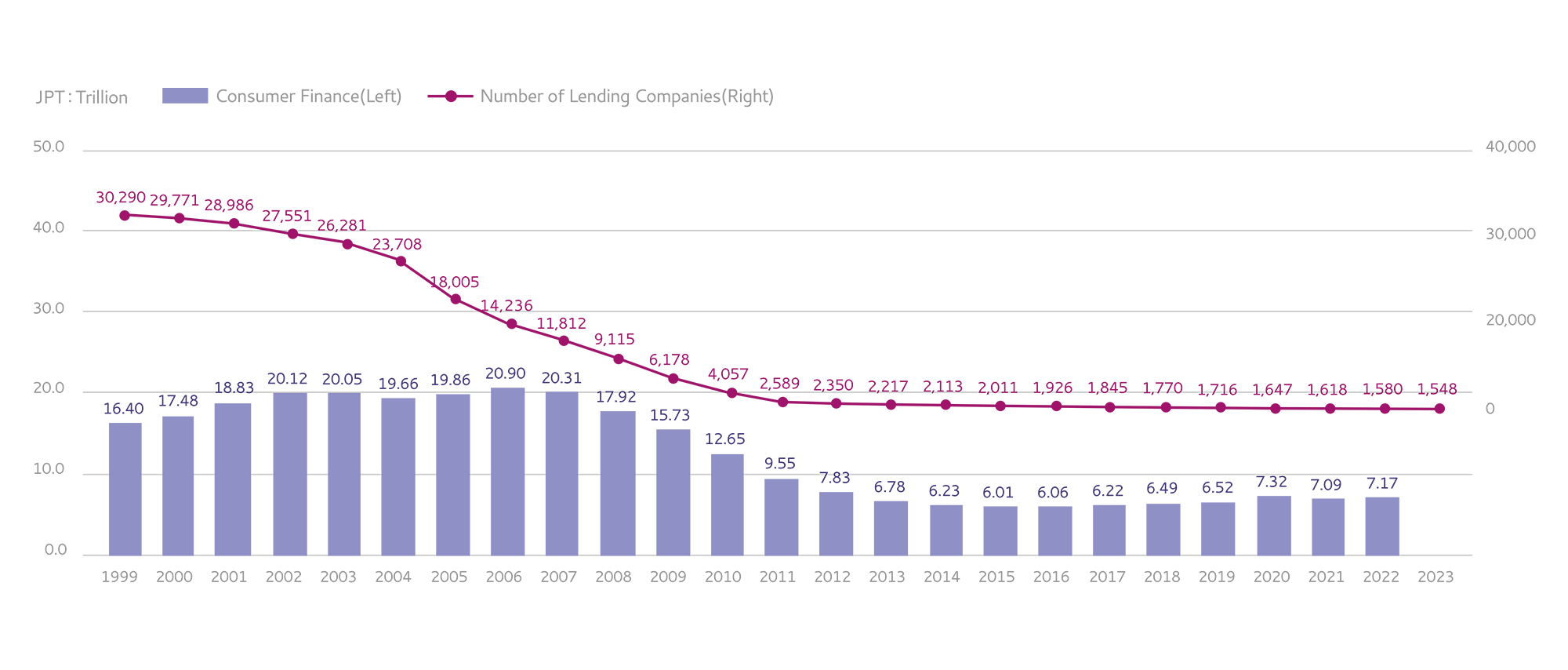
Historical Lending Market Tendency
As shown below table, consumer finance outstanding drop to 1/3 and number of players drop to 5% from the peak.
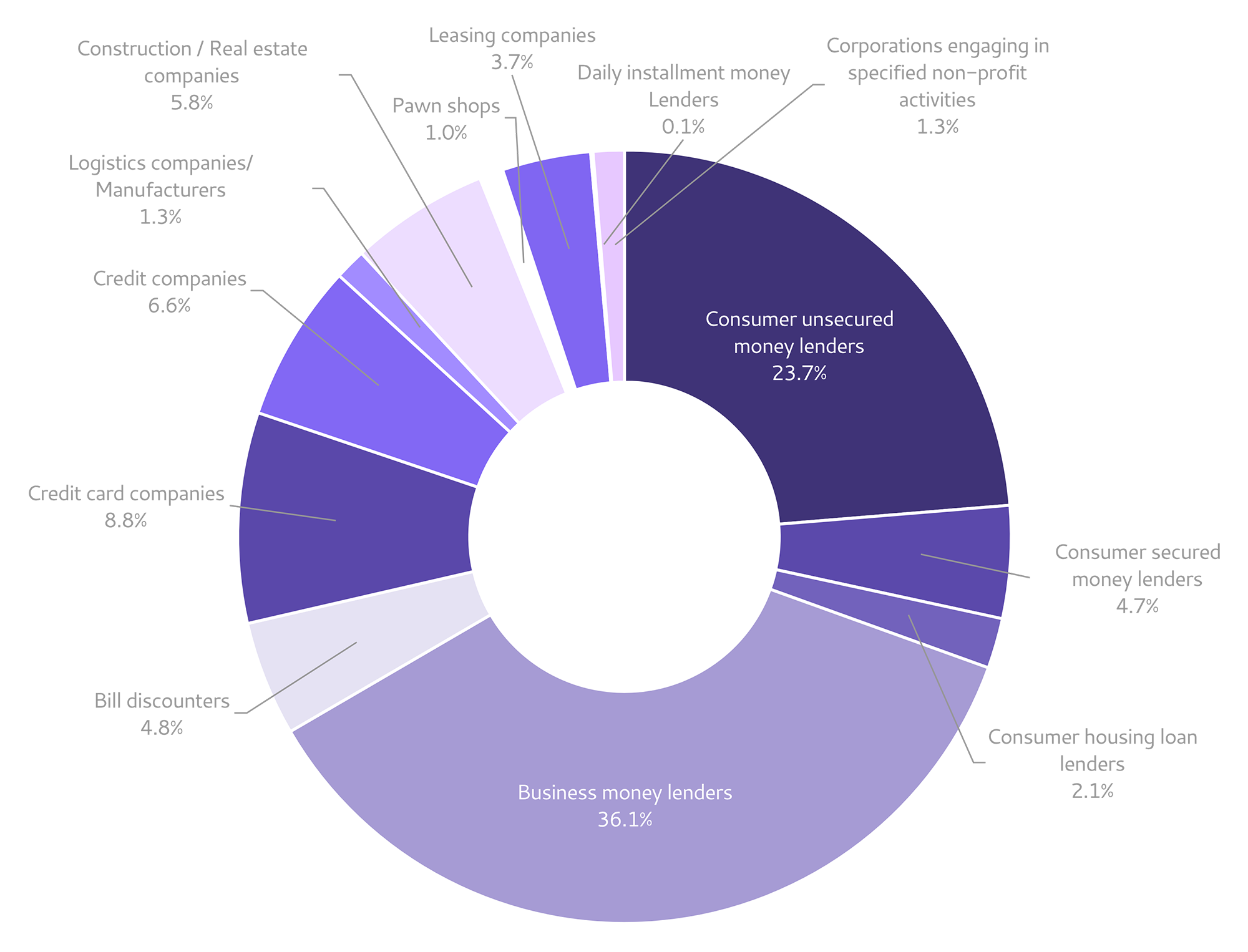
Diversified money lenders that support people's lives and business activities
Money lenders have a variety of business types and business forms. There are over 1,600 money lenders across the country, each with their own characteristics to meet the various urgent financial needs of general consumers (individuals) and businesses.
Many people get the benefits from money lending services.
Japanese population aged 20 and over is 104.87 million. Of these, 10.16
million people use money lending services.
- One in ten people uses money lending
services.
- On average, people borrows from 1.5 companies.
- The average borrowing
amount per contract is 574,000 yen. (For unsecured, unguaranteed loan, 540,000 yen)

